Green Wall and Rooftop Gardening
Green Wall and Rooftop Gardening
From ancestorial times greening of outside walls and roofs of buildings has taken place for environmental harmony. Societies are in a need for making a conscious choice to switch to a more sustainable way of life.
The reason for doing so was the increase of insulation, improved aesthetic value, enhance indoor and outdoor climate, reduce greenhouse gases as well as increased ecological values by creating habitat for birds and insects. The green roof provides shade, removes heat from the air, reduces the temperature of the roof surface, and improves surrounding health. It is also seen that doctors are increasingly prescribing for spending time gardening to patients dealing with anxiety and depression. Spending time gardening can provide mental peace. Green walls feel the soul with joy. Green encourages a balance in your brain that leads to decisiveness. People can also get organic vegetables by growing them on the roofs of buildings.
Urban
Gardening:
Urban Gardening is a practice through
which people grow plants and crops in and around the cities in urban and peri-urban localities. Urban gardening is where people practice cultivation, mainly
of vegetables, and flowers in and around urban areas. Basically, it is the traditional
cultivation of crops, but in urban centers. With urbanization and since more
and more people would like to do their farming where they are, urban gardening
is considerably been taken up and has been a successful alternative; a shift
from the traditional thinking that cultivation of crops can only be done in
rural areas. Urban gardening is hence a venture that helps urban
communities in social, economic, and healthy ways of living, by stimulating the
local economy and also serves as an effective means of securing a family’s food
security.
GREEN
WALLS
Green walls are partially or fully wall-embedded vertical gardens. It is a vertical structure built against an existing
wall, both on the interior and exterior of the building. One of the most significant
benefits of a green wall is to improve the quality of your indoor air. Approximately
25% of carbon emissions made by human activity are absorbed by plants and
living walls. Plants on the wall filter toxins in the air and convert carbon
dioxide to oxygen. Green walls are the living walls of the house. The structure is
attached to the existing wall at various points and then planted with lots of
beautiful greenery. These greeneries are planted in a medium such as soil, vermiculite,
perlite, cocopeat, rock wools, or water.
Types of Green Walls
1. Wall
climbing green wall- It is a very common and traditional green
wall method. Although it is a time-consuming process, climbing plants can
cover the walls of the building naturally.
2. Hanging
down green wall - The hanging down type is also another
popular approach for green walls. It can easily form a complete vertical belt
on a multistorey building through planting at every story compared to the wall
climbing type.
3. Module
type green wall- The module type is the latest concept
compared to the previous two types. It requires a more complicated design and it
is probably the most expensive green walls method.
Benefits
of Green Walls
·
Living green walls purify the air.
·
Green walls increase the feeling of
well-being.
·
A living green wall reduces the ambient
temperature.
·
Reduces ambient noise.
·
Green walls reduce stress.
·
Green places show a longer residence time.
·
Living walls offer a powerful healing
environment.
The rooftop garden is a garden on the roof of the building. Besides the decorative benefit, roof planting provides food, control
temperature, hydrological benefits, architectural enhancement, habitats or
corridors for wildlife, recreational opportunities, and on a large scale it may
even have ecological benefits. Rooftop gardens are man-made green spaces on
the topmost levels of industrial, commercial, and residential structures. They
may be designed to grow to produce, provide play space, give shade and shelter, or
simply be there as a living green area. Rooftop gardening comes with a
plethora of advantages like sustainable production, decreasing family monthly investment,
improving the quality of air in the roof, and providing healthy nutritious vegetables
straight from roof to plates.
Types of Roof Top Gardening-
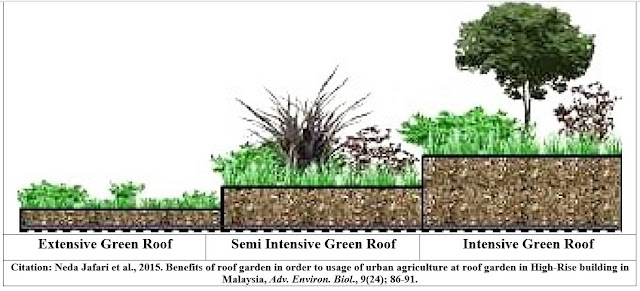
1. Extensive
green roof- It is a low-maintenance green roof garden that has a
thin, lightweight growing medium. This type of green roof is characterized by
its vegetation, which is often limited to sedums, mosses, herbs, small plants
and flowers, dessert grasses, and succulents because it has a growing medium
depth of around 3-6 inches, an extensive green roof is easier to install and
cost-efficient and generally does not require an irrigation system to survive.
It is ideal for stormwater management for flat or low-sloped roofs and
retrofits.
2. Semi-intensive green roof- It is a mix of both intensive and
extensive green roofs. It is characterized by a growing medium depth of around
6-12 inches to host a much richer ecology. Greenery in this type of rooftop
garden consists of small plants, grasses, herbs, small shrubs, and ground covers
that require occasional irrigation and moderate maintenance.
3. Intensive
green roof- It is more of a rooftop garden or sky park than
anything else. This roof garden design is characterized by deep soils that have
a growing medium depth of more than 6 inches, A variety of vegetation can be
grown in an intensive roof garden, from small to large plants, shrubs, ground
covers, and even small trees.
Benefits
of rooftop garden-
·
It reduces the heat of buildings and
energy costs.
·
It creates a habitat for wildlife.
·
It reduces ambient temperature.
·
It captures and harvests rainwater.
Conclusion-
“The
greener the setting the more the relief”. We call this our “Balanced flow”
because the living walls will give you the peace and harmony that you need to
continue with your day! Whether you pause to look at it and breathe in the green
or just pass by it on the way, you will feel a sense of relief.
Authors: Kajal Jaiswal and S. Mishra (IAS, SOADU)


Join the conversation